- AustraliaEnglish
- BelgiumDutchFrench
- BrasilPortuguese
- CanadaEnglish
- FranceFrench
- GermanyGerman
- GlobalEnglishFrenchSpanish
- GreeceGreek
- IndiaEnglish
- ItalyItalian
- JapanJapanese
- LuxembourgFrench
- Middle East & AfricaEnglish
- NetherlandsDutch
- PolandPolish
- PortugalPortuguese
- SpainSpanish
- SwedenSwedish
- TurkeyEnglish
- United KingdomEnglish
- United States of AmericaEnglish
PV and Solar Inverters
A solar or photovoltaic inverter is an essential component of PV systems. What does a solar inverter do? A solar inverter for solar panels converts the direct current (DC) generated in the PV modules into alternating current (AC). Solar inverters by SMA are compatible with the PV modules from leading manufacturers. And we offer the right inverter for any application − whether household, business or industry – as well as different solar inverter sizes and solar inverter types, e.g. a solar inverter 10 kW or a solar inverter 10 kw. Learn more about our innovative technology here.
SMA Status Update: Australian Requirements
SMA PV inverters
SMA Home & Commercial Energy Solution, String Inverters
Sunny Tripower 3-6 3 kW / 4 kW / 5 kW / 6 kW
Three-phase solar inverter for private households.
Sunny Tripower 8-10 8 kW / 10 kW
Maximum yield for household systems and small commercial applications.
Sunny Tripower X 12 kW / 15 kW / 20 kW / 25 kW
Energy generation and management for larger households and commercial PV systems.
SMA Large Scale Energy Solutions, Central Inverters
What is a PV inverter?
Every PV system requires at least one inverter. While the electricity grid supplies alternating current (AC) and most home appliances function with alternating current, the PV modules on the roof produce direct current (DC). This direct current must be converted into alternating current (AC) for everyday use. Otherwise, it is not possible to use the self-generated energy or to feed into the electricity grid.
Inverters − easily explained
Inverters are frequently referred to as the "heart" of a PV system because they play a central role in the conversion of the generated direct current into usable alternating current. Without an inverter, efficient and reliable use of the solar power generated by the PV system would not be possible. PV inverters are also the link between the PV modules on the roof and the private electricity supply in the house on one hand and the electricity grid on the other.
PV and solar inverters: Models and versions
PV and solar inverters are available in different versions for a variety of applications. The following inverter types are most commonly used:
Micro inverter (solar panel) / Module inverter
These inverters for PV systems are directly connected to the PV modules: there is one PV inverter connected to each PV module. The micro inverter for solar panels are frequently used in small PV systems such as balcony power plants.
String inverters
In larger PV systems, the individual PV modules are switched successively in series (as a string). Instead of equipping each module with its own solar inverter, so-called string inverters are used here. These convert the entire direct current (DC) generated by a module group into alternating current that can be used and fed into the grid. A multistring inverter combines the energy flow of several module strings and converts the generated energy from direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
Central inverters
Large photovoltaics ground-based PV systems, also called PV or solar farms, usually have hundreds of PV modules. Central inverters are used here, which bring together the strings of all modules and convert the direct current (DC) they generate into alternating current (AC). The central inverter is frequently located in its own technical service room.
Battery inverters
Battery inverters are devices that are used in PV systems with battery storage systems to convert the direct current (DC), which is stored in the batteries, into alternating current (AC). This conversion allows the stored energy from the battery to be provided for the use in a household or to be fed into the electricity grid.
Hybrid inverters
Hybrid inverters from SMA combine the functions of a PV inverter with those of a battery inverter in a single device.
How does a solar inverter work?
In the PV system, the inverter has an important job: when the solar radiation hits the PV modules, they convert the energy into direct current (DC). However, this direct current can neither be used in the household nor can it be fed into the electricity grid. That is why each PV system requires a photovoltaic inverter:
The direct current (DC) generated by the PV system is transferred to the PV inverter via a cable.
The inverter converts the direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
The alternating current can be consumed in the household or business or fed into the electricity grid.
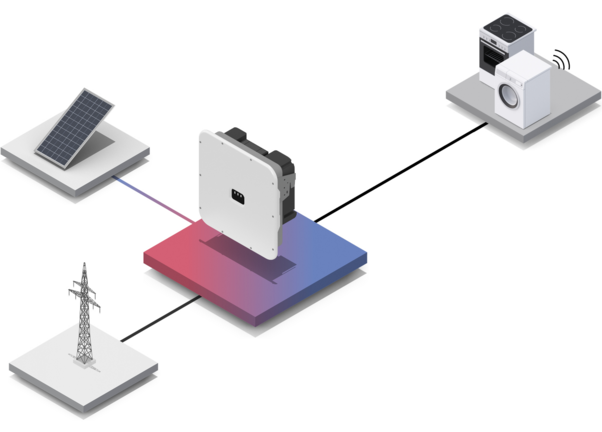
Photovoltaic inverter converts direct current into alternating current
Alternating current is supplied to consumers
Direct current is generated by inverter solar panels
Alternating current is fed into or drawn from the utility grid
Advanced functions of SMA solar inverters
In addition to this basic function, an SMA PV inverter also takes care of many other tasks. The most important functions include:

Yield and PV system monitoring
Monitoring the PV system and checking the yields achieved do not have to be complicated. A SMA solar inverter for home use with Home Management System is easily controlled from a smartphone or tablet. All yield data is available to you conveniently and concisely in Sunny Portal and the SMA Energy App.

Grid monitoring
SMA PV inverters ensure that the voltage and frequency remain consistent when the self-generated energy is fed into the household grid.

Power optimisation
With SMA ShadeFix, a solar/photovoltaic inverter from SMA always gets the most out of the PV modules – even if there is dirt or shading. SMA ShadeFix is supported by MPP trackers. MPP tracking stands for "Maximum power point tracking". This means that SMA PV inverters adapt the electrical load in each PV cell/module so that each cell can supply the greatest possible power.

Safety
Safety is a top priority at SMA in the design and sale of the photovoltaic inverters. Our concept for the safe operation of PV systems relies on various components that perfectly complement each other:
Lean PV systems with high-quality devices
Intelligent and innovative software features
Extensive testing and quality inspections
40 years of global experience in PV technology development
Hands-on training for first-time PV owners and professionals
Difference between a PV inverter 3-phase and 1-phase
There are single-phase and three-phase inverters that differ as follows:
PV inverter 1-phase
Single-phase PV inverters are connected to a power line or line conductor. They are comparatively efficient and suitable for small PV systems.
PV inverter 3-phase
Three-phase inverters are connected to three power lines or three line conductors. They are more powerful, more energy efficient and more versatile.
In early 2012, German lawmakers defined a so-called Application Rule (VDE-AR-N 4105) to ensure maximum grid stability for the operation of PV systems. This regulation states that single-phase inverters can now be used up to a system size with an apparent power of 4.6 kilo-volt amperes (kVA). If the apparent power of the PV system exceeds 4.6 kVA, the use of a three-phase inverter is required. This is one of the reasons why three-phase inverters are now being used more frequently in Germany.
The three-phase inverter is also increasingly the norm in Austria and Switzerland. The single-phase inverter is used in small PV systems and is more of an exception.
How do you select a suitable photovoltaic inverter?
The selection of the right photovoltaic inverter depends on many factors and is therefore usually made by experts. An overview of the most important steps:
First, the maximum power is determined that the PV system can generate under ideal conditions. Then a photovoltaic inverter or a solar inverter for solar panels is selected that supports this direct current output.
If surplus electricity is to be fed into the electricity grid, a grid-tied PV inverter is required. If no grid feed-in is planned, an off-grid PV inverter for stand-alone mode is the right choice.
A decision is made as to whether the PV inverter should be three-phase or single-phase.
The next step is to compare the solar inverter efficiency of the models in question. The more efficiently the PV inverter works, the higher the energy yield and the lower the losses.
The compatibility of the desired photovoltaic inverter with the installed or planned PV modules must be checked.
The solar inverter installation site must also be taken into account when selecting a PV inverter. Not every model is suitable for all temperature ranges (e.g. summer heat in the attic) or humidity (e.g. in an outdoor installation).
Ease of use and software features also play an important role in the selection process. SMA solar inverters are intuitive to operate and optimise the performance of PV systems using intelligent control.
SMA solar power professional search
For a custom energy system, it is best to seek advice from a qualified specialist company.

Connecting the inverter
The installation of a PV inverter or solar inverter for solar panels should be well planned and always carried out by appropriate solar power professionals. When connecting, follow all instructions in the valid operating manual for your device. The following points are particularly important:
Ideally, the photovoltaic inverter is installed in a dry, well-ventilated location that is frost-free and protected from sunlight.
Placement close to the building’s main circuit reduces the labour and cost of connection.
Wiring must be carried out with special solar cables that can withstand the high electrical currents that the solar cells produce with good solar irradiation.
The shortest possible cable routes with the widest possible cross-section ensure that the module output can be fully utilised.
Frequently asked questions about PV / solar inverters
How big does the inverter have to be in a PV system?
The PV inverter must correspond to the maximum direct current output of the PV system. Oversized devices are not a problem but too little capacity is.
How long will an inverter last in a PV system?
Depending on the model, SMA solar inverters are designed for an operating life of around 25 years.
How much electric current does a photovoltaic inverter consume?
Regarding the PV inverter price and cost: The power consumption of a solar/photovoltaic inverter depends on power and model. During the day, the device draws its energy from the PV system. This means that electricity costs are only incurred for the open-circuit operation at night. The power consumption is very low though; for a Sunny Tripower X it is less than 5 watts, for example.
How many PV modules can be connected to an inverter?
The number of PV modules that can be connected to a solar or hybrid inverter depends on the power of the individual PV modules and the power class of the inverter.
For example: If the PV system consists of 10 modules connected in series, each with a power of 300 W, the maximum peak power is 3 kW. An inverter with a power of up to 3 kW should be used for a system of this kind.
For the majority of the time, the PV system does not produce at full capacity, because the sun does not always shine consistently and the modules may be shaded. Although SMA ShadeFix optimises the power, full power cannot always be achieved, so the system might be oversized in comparison with the inverter. This means that, under certain conditions, an inverter with a power of 2 kW can be sufficient for a system with a peak output of 3 kW. An oversized PV generator is especially useful for hybrid inverters. This means more surplus power can be stored directly in the battery and is not lost.
The optimum power class of the inverter depends on the specific characteristics of the PV system. PV installers can make more exact calculations using tools such as Sunny Design.
Can a PV system also be operated without an inverter?
In theory, a PV system can be connected without solar inverters. This is common in small, mobile systems, e.g. for motorhomes. These portable modules feed the board battery with direct current. However, with PV systems in homes without inverters, the entire household would have to be modified to loads that work with direct current (DC). A complex modification would be necessary.
What is the difference between inverters that feed into the grid and a PV inverter off-grid or a solar inverter off-grid?
Battery inverters (off-grid) are not meant to be connected to the electricity grid; the solar power produced on the roof is exclusively consumed by the owner. Solar inverters that feed into the grid, on the other hand, feed unused solar power into the electricity grid. Owners of such a system will receive a feed-in tariff in return.




